Product
Granular Activated Carbon Regeneration System
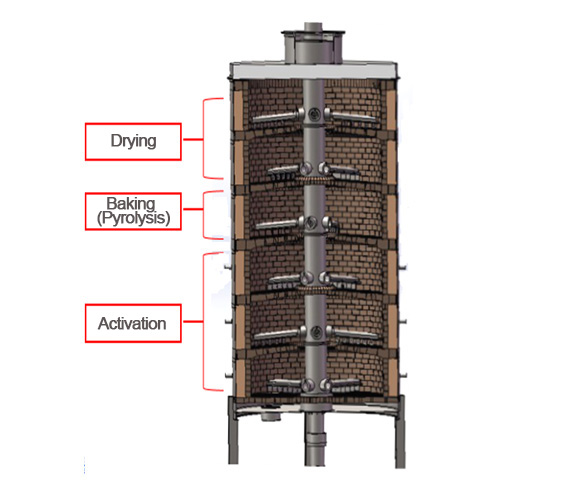
Drying
Stages 1-2: (100~300°C) Moisture evaporation and drying within the activated carbon.
Drying Process
Stage 3: (400~600°C) Volatiles from organic substances adsorbed in the pores of the activated carbon are evaporated and carbonized.
Activation Process
Stages 4-5: (800~1000°C) Steam is blown in to remove carbides from the pores of the activated carbon formed during the baking process, restoring the activity of the activated carbon.
Activation Process
Can be paired with upstream wastewater adsorption processes to form a continuous adsorption-regeneration process system for wastewater applications. 5. Can be combined with upstream decolorization processes to form a continuous decolorization-regeneration process system for applications like syrup, alcohol decolorization, etc.
Activation Reaction
C+H₂O→CO+H₂
